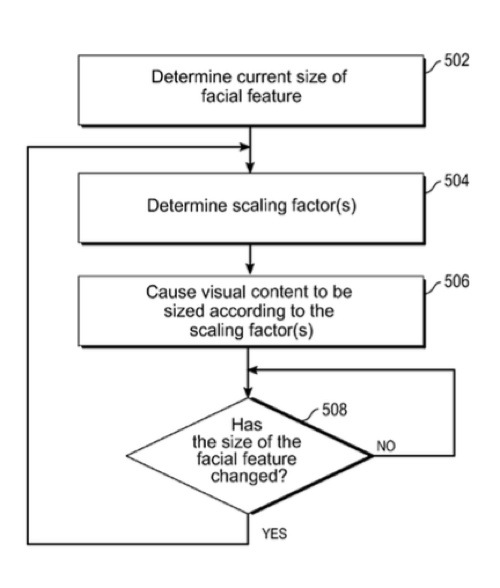
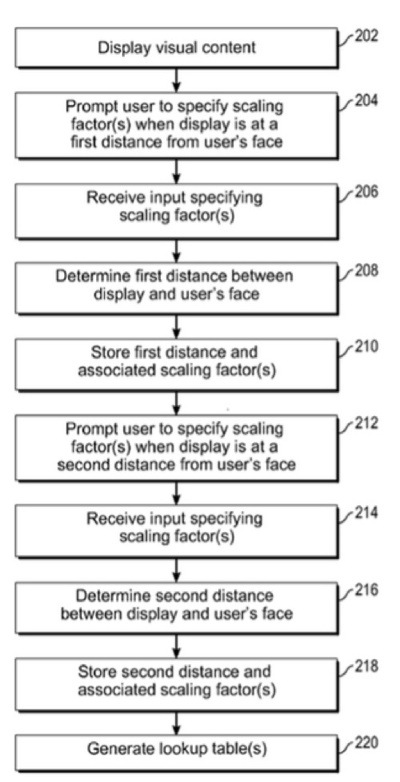
Would you like your iPhone or iPad to expand or shrink on-screen images depending on how close it is to you? That could eventually be possible. A new Apple patent (number 20120287163) is for mechanism for automatically scaling the size of a set of visual content based upon how close a user's face is to a display.
In one implementation, the mechanism initially causes a set of visual content on a display to be sized according to a first scaling factor when the user's face is at a first distance from the display. The mechanism then determines that the user's face has moved relative to the display such that the user's face is no longer at the first distance from the display. In response, the mechanism causes the set of visual content on the display to be sized according to a second and different scaling factor. By doing so, the mechanism effectively causes the display size of the visual content to automatically change as the distance between the user's face and the display changes.
Here's Apple's background on the invention: "Many of today's computing devices allow a user to scale the visual content that is being displayed to a size of the user's liking. For example, some smart phones and tablet computing devices allow a user to put two fingers on a touch sensitive display and either pinch the fingers together or spread them apart. Pinching the fingers together causes the display size of the visual content to be reduced, while spreading the fingers apart causes the display size of the visual content to be enlarged. By adjusting the scale of the visual content, the user can set the visual content to a size that is comfortable for him/her.
"Often, during the course of using a computing device, especially one that is portable such as a smart phone or a tablet, a user may position the display of the computing device at different distances from the user's face at different times. For example, when the user starts using a computing device, the user may hold the display of the computing device at a relatively close distance X from the user's face.
"As the user's arm becomes fatigued, the user may set the computing device down on a table or on the user's lap, which is at a farther distance Y from the user's face. If the difference between the distances X and Y is significant, the scale of the visual content that was comfortable for the user at distance X may no longer be comfortable for the user at distance Y (e.g. the font size that was comfortable at distance X may be too small at distance Y).
"As a result, the user may have to manually readjust the scale of the visual content to make it comfortable at distance Y. If the user moves the display to different distances many times, the user may need to manually readjust the scale of the visual content many times. This can become inconvenient and tedious."
The inventor is Amir Djavaheerian.
Also appearing today at the U.S. Patent & Trademark Office are:
° Patent number 20120290113 for seamless switching between radio and local media;
° Patent number 20120284779 for electronic devices having adaptive security profiles and methods for selecting the same;
° Patent number 20120290864 for systems and methods for asynchronous management of access requests to control power consumption;
° Patent number 20120290336 for systems, methods, and devices for providing event-related incentives;
° Patent number 20120289265 for remote messaging for a mobile communication device and accessory;
° Patent number 20120288089 for a system and method for device dependent and rate limited key generation;
° Patent number 20120287149 for a system and method for processing graphic operations on a plurality of data structures of an image with a graphics processing unit and memory;
° Patent number 20120287149 for a method of operating a computing device to provide presence based functionality.